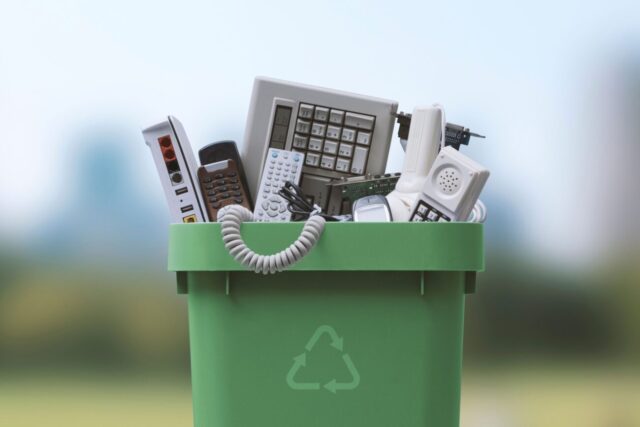
Electronic waste, or e-waste, refers to discarded electronic appliances such as mobile phones, computers, and televisions. As technology progresses at a rapid pace, the lifecycle of these products has significantly shortened, leading to an increase in waste. Managing this waste is critical, but why should we care?
Environmental Protection
One of the primary reasons for managing electronic waste recycling is to protect our environment. Electronic devices contain toxic substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium.
When disposed of improperly, these chemicals can leach into the soil and water, contaminating them and causing harm to plants, animals, and humans. E-waste recycling and proper disposal prevent these toxins from causing environmental damage.
Human Health Concerns
The health implications of e-waste are substantial. Workers in informal e-waste recycling centers are often exposed to hazardous substances. Without proper safety measures, they can suffer from respiratory issues, skin conditions, and other serious health problems. Additionally, communities living near e-waste dumps can experience health issues due to exposure to toxic materials.
Resource Conservation
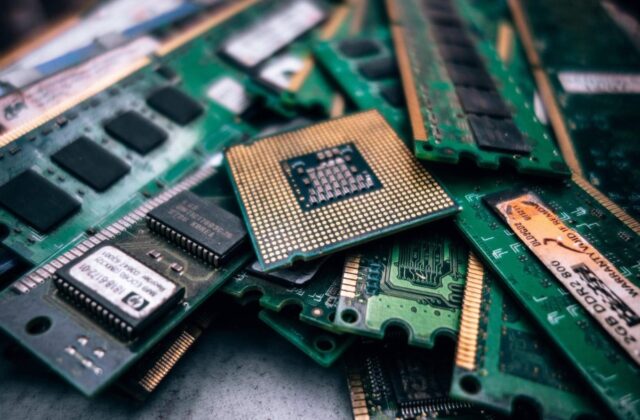

E-waste contains valuable materials such as gold, silver, copper, and rare earth metals. Efficient recycling can recover these resources and reintroduce them into the manufacturing cycle.
This reduces the need for mining, conserves natural resources, and saves energy. By managing e-waste, we ensure that these precious materials are not wasted but used to their fullest potential.
Economic Benefits
Recycling and managing e-waste also provide economic advantages. It creates jobs in the recycling industry and generates revenue from recovered materials. Moreover, it promotes innovation in recycling technologies and can lead to the development of new business models and economic growth.
Data Security
Electronic devices often hold sensitive information. Improper disposal of e-waste can lead to data breaches and identity theft. E-waste management includes the secure destruction of data storage devices, ensuring that personal and corporate information remains confidential.
Sustainable Development
Lastly, e-waste management is integral to sustainable development. It encourages the production and consumption of electronics in an environmentally and socially responsible way.
By incorporating e-waste management into sustainable practices, we can promote a circular economy where products are designed to be recycled and reused, reducing waste and the strain on the environment.
Promoting Innovation and Infrastructure
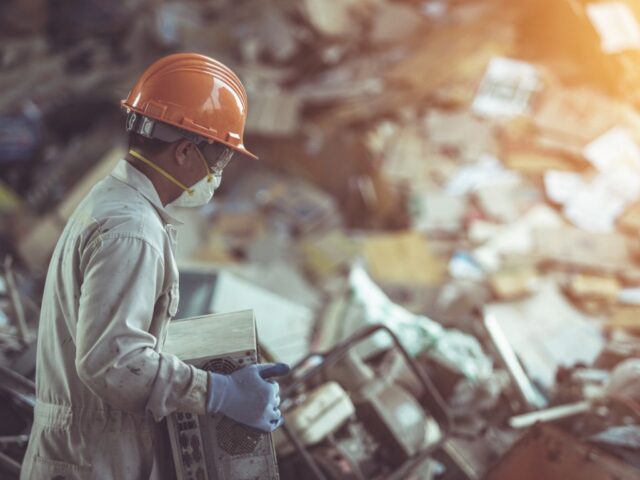

An often overlooked aspect of e-waste management is its potential to drive innovation and improve infrastructure. As the demand for responsible e-waste disposal rises, there is a growing need for innovative solutions that can enhance recycling processes and create more sustainable products. This drives research and development in new technologies that can efficiently extract valuable materials from e-waste or find novel uses for recycled components.
Furthermore, managing e-waste responsibly encourages investment in recycling facilities and infrastructure that can handle the complex process of dismantling, sorting, and processing electronic waste. Such infrastructure is not only essential for the recycling process but also contributes to the development of a skilled workforce trained in the latest recycling and waste management techniques.
By focusing on e-waste, we also pave the way for advancements in product design. Manufacturers are encouraged to design products with longer lifespans and easier recyclability, contributing to the reduction of e-waste generated. This shift towards designing for the environment can lead to more sustainable consumption patterns and a decrease in the environmental impact of electronic goods.
In conclusion, effective e-waste management spurs technological and infrastructural advancements that can have a far-reaching impact on our economy and environment. It is an investment in a cleaner and more technologically advanced future.