The nervous system is the system that plays a dominant role in the regulation of physiological functions in the body and is mainly composed of nerve tissue, divided into two major parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral system includes the cerebral and spinal nerves.
Neurological diseases, a small group of medical conditions that affect the nervous system, are more than 600 different diseases, including genetic disorders, infections, cancers such as epilepsy, cardiovascular diseases, congenital and developmental disorders (such as spina bifida) and degenerative diseases (such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis), among others, which often leave doctors at a loss.
However, recent studies have shown that a drug called 7,8-dihydroxyflavone significantly affects the treatment of neurological disorders. Here we will give you more details about this great drug.
What is 7,8-dihydroxyflavone?
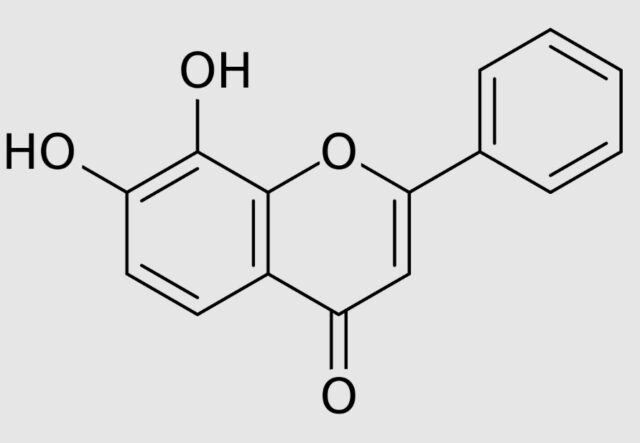
7,8-dihydroxyflavone, also known as Tropoflavin, is a naturally occurring flavonoid found in the leaves of Godmania aesculifolia, Tridax procumbens and Primula trees. 7,8-dihydroxyflavone is a dihydroxyflavone substituted at 7th and 8th positions by 7,8-dihydroxyflavone is a dihydroxyflavone substituted with a hydroxyl group at the 7th and 8th positions.
In animal models, it has shown efficacy in several nervous system diseases, including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s. It acts as a plant metabolite, tropomyosin-related kinase B receptor agonist, antidepressant, antioxidant, and antitumor agent.
Role of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone in neurological disorders
According to recent scientific studies, 7,8-dihydroxyflavone has been shown to have a significant therapeutic effect in various central nervous system disorders, including depression, Alzheimer’s disease, cognitive impairment in schizophrenia, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, cerebral ischemia, fragile X syndrome, and Rett syndrome.
What is fragile x syndrome? Intellectual disability, anxiety disorders, social phobia, behavioral and learning difficulties, as well as a variety of physical traits, are all symptoms of the rare genetic illness FXS. Both inherited intellectual disability and autism spectrum disease have it as their primary genetic cause.
In addition, 7,8-dihydroxyflavone has shown efficacy in animal models of age-related cognitive impairment and enhanced memory consolidation and emotional learning in healthy rodents.
Furthermore, 7,8-dihydroxyflavone possesses potent antioxidant activity independent of its action on TrkB receptors and protects against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity, and oxidative stress-induced genotoxicity.
It was also found to block methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity, and unlike those above, this effect is thought to be TrkB-dependent. The highly hydroxylated analog, gossypetin (3,5,7,8,3′,4′-hexahydroxyflavone), is an antagonist of TrkB.
Research Directions for 7,8-dihydroxyflavone
Benchchem scientists have found that 7,8-dihydroxyflavone inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase and estrogen sulfotransferase. This drug also reduces sleep in mice during the dark phase and decreases orexin-A levels in the hypothalamus but not orexin-B.
Because of 7, 8-dihydroxyflavone’s neurological due to the critical role of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone in the nervous system, it is believed that shortly, 7,8-dihydroxyflavone will have more application prospects.