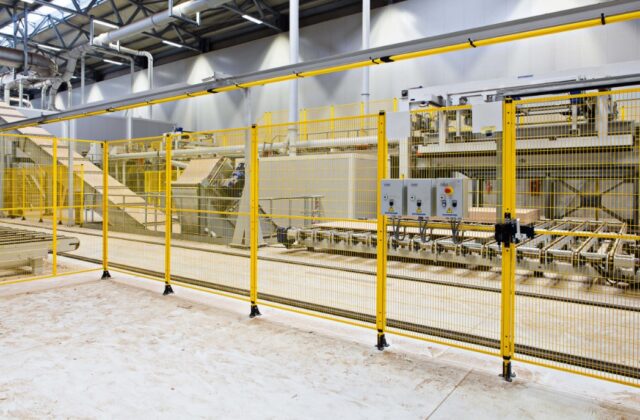
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set forth specific machine-guarding requirements that employers must follow to ensure the safety of their employees.
Employers are responsible for implementing guards or barriers on machines to protect workers from potential injuries, such as amputations, crushed hands, fingers, toes, lacerations, punctures, and Burns.
There are general requirements for all types of machinery and specific requirements depending on the type of machine. Guards must withstand forceful contact with parts of the body and debris created by the machine’s moving parts. The National Institute for Optimum Safety in Manufacturing recommends that these guards resist flames where appropriate.
According to OSHA regulations 1910 Subpart S Machine Guarding: General Requirements, guard design should consider human engineering principles “such as reach ranges, natural work postures, and motions.” In other words, manufacturers should consider how people naturally interact with equipment when designing effective guards. For example, washers/dryers tend EU16 grab onto clothes – meaning if there were no safe waypoint within reach – say 6 inches higher than top-of-machine guardrail height – persons reaching into use article would do so dangerously.
There are numerous OSHA machine guarding requirements, which can vary depending on the particular type of machinery. In general, however, employers must ensure that all machines have adequate guards to protect workers from contact with moving parts or other hazardous elements. Additionally, these guards also resist flames where appropriate.
General Information About Guards

OSHA machine guarding requirements mandate various types of guards to protect workers from contact with hazardous elements on machinery. In general, these guards must be in place whenever employees are working with or near the machines. The specific type and height of the guard will depend on the particular hazard being guarded against.
Flame-resistant materials may also be required where appropriate to prevent injuries in case of an accidental fire. Guards should always be inspected regularly for damage or wear and replaced as necessary to keep workers safe.
Types Of Machines That Require Guards
A guard is one of the most important safety equipment in any industrial setting. Guards are essential to preventing injuries in case of an accidental fire or machine malfunction, and they should always be inspected regularly for damage or wear and replaced as necessary.
Many different types of guards can be used in an industrial setting, but the specific hazards each one is designed to protect against vary depending on the type of machine it’s installed on. Some common types include:
- Fixed Guards (metal mesh) need to be used on machines with a danger of contact with moving parts.
- Movable Guards (doors) need to be used along with the fixed guards to provide access to the machines when it’s safe.
- Mechanical Locks must be used on machine guarding doors to ensure that they cannot accidentally open and create a hazard.
- Finally, Interlocks must be used on safeguarding doors to prevent them from being opened while the equipment is running.
Each type has its specific purpose, so employers must understand which ones are required for their machines. The following is a brief overview of some common machines that require guards according to OSHA standards:
- Machinery with moving parts – This includes machinery like presses, mills, and grinders, which have variable speed controls and pose a danger if someone comes into contact with them while running. To prevent potential injuries, guards should be installed on all sides of these machines (including the top).
- Portable grinding wheels – These tools can cause serious injuries if someone comes into contact with them while rotating, so guards should be placed on all sides of the grinding wheel to protect workers.
Specific OSHA machine guarding requirements must be followed when using certain machinery. Guards should be placed on all sides of machines, such as grinders, saws, and lathes, to protect workers from potential injuries.
The Purpose Of Guards On Machines
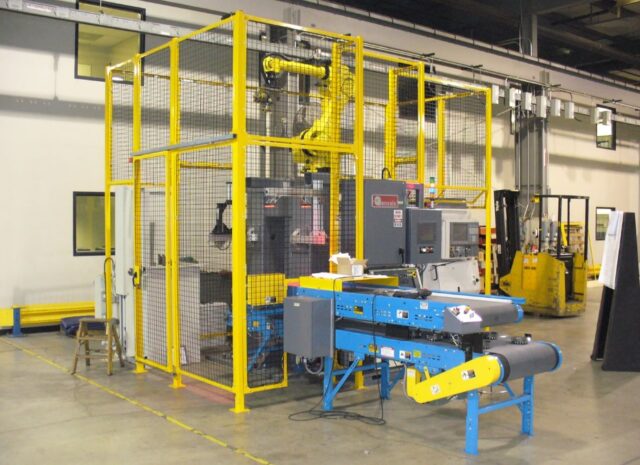

Safety is of the utmost importance when using certain machines in a factory or manufacturing setting. To protect workers from potential injuries, guards should be placed on all sides of machines, such as grinders, saws, and lathes. This is mandated by OSHA machine guarding requirements which must be followed when using this equipment.
Guards serve two main purposes: they prevent accidental contact with moving parts on the machine and shield people from flying debris that may come off the machinery while it’s in use. Employees must be properly trained on how to use a particular machine safely – including knowing what hazards to look out for – before being allowed to operate it unsupervised.
Accidents can occur easily if proper precautions aren’t taken when working with machinery, so following OSHA machine guarding requirements is essential for keeping everyone safe. By ensuring that guards are in place and functioning properly, employers can help reduce the risk of an accident and keep their workforce free from harm.
Are There Any Exceptions To Using Guards On Machines?
There are some exceptions to using guards on machines, but they are mainly limited to specific circumstances. For example, if a guard would get in the way of the machine’s normal operation or if it is not possible to install one due to the design of the machine, then it may be permissible to operate without it. In certain cases, an operator can also be trained to use a machine safely without a guard in place – as long as this is properly documented and everyone involved is aware of the risks.
However, employers should remember that these exemptions are only made under specific conditions and that safety must always come first when working with machinery. Guards should always be used whenever possible, and operators must receive proper training to safely work with any particular machine before being allowed unsupervised access.

Conclusion
Every year, thousands of people are injured in machine-related accidents. Many of these injuries could have been avoided if employers had followed OSHA machine guarding requirements. These guidelines protect employees from hazards such as dangerous moving parts or exposure to hazardous chemicals when working with machinery.
All workers must be properly trained to use machines safely before being allowed to operate them unsupervised. This includes knowing what hazards to look for and taking the necessary precautions to avoid injury. Accidents can occur easily if proper precautions aren’t taken. Employers must follow OSHA machine guarding requirements closely and ensure their workforce is fully aware of the dangers of using machinery.